Why is Reagan Bush ’84 So Popular?
In November 1984, the United States witnessed one of the most decisive presidential elections in its history. The question many scholars, students, and political observers ask today is: Why is Reagan Bush ’84 so popular? This landmark election saw President Ronald Reagan and Vice President George H.W. Bush secure a resounding victory against their Democratic opponents. The result was not just a win in numbers; it symbolized widespread public enthusiasm, cultural momentum, and enduring political influence. To understand the full scope of this popularity, we must examine economic, social, historical, and media factors that made Reagan Bush ’84 an enduring symbol of American political success.
The Context: America in the Early 1980s
To answer the question why is Reagan Bush ’84 so popular, it’s essential to look at the circumstances of the period. The late 1970s and early 1980s were marked by inflation, high unemployment, and geopolitical tension. Many Americans were frustrated with what they saw as stagnation and decline. Reagan’s presidency arrived with promises of strong leadership, economic revival, and renewed national confidence—an offer that appealed to millions who were desperate for change.
Reagan’s Leadership Style: A Central Component
One of the primary reasons why Reagan Bush ’84 is so popular lies in Reagan’s leadership characteristics. Reagan was a communicator at heart. His optimism, charisma, and ability to connect with everyday Americans earned him the nickname “The Great Communicator.” Rather than political speeches laden with jargon, Reagan spoke in a straightforward, relatable manner, which helped his message resonate widely.
Authenticity and Persona
Reagan’s background as an actor worked to his advantage; he understood not just politics but presentation. Yet, unlike many polished politicians, he appeared authentic—a key factor in public appeal. This charisma has become one of the least tangible yet most important parts of understanding why Reagan Bush ’84 so popular.
Economic Performance: “Morning in America”
Economists and voters alike point to the economy as one of the strongest reasons why Reagan Bush ’84 so popular. After a recession at the beginning of Reagan’s first term, the economy entered a period of sustained growth. Unemployment began to fall, interest rates stabilized, and business investment increased.
The Power of the Campaign Slogan
Part of Reagan Bush ’84’s popularity stemmed from its optimistic messaging. The campaign’s iconic slogan, “Morning in America,” captured a sense of rejuvenation. Rather than offer fear-based warnings, the campaign highlighted recovery and hope. This positive framing not only attracted voters at the time but has also shaped Reagan’s long-term image in history.
Strong National Security Stance
Another important piece of the popularity puzzle was Reagan’s approach to national security. The early 1980s were deep into the Cold War, and Reagan’s strong anti‑Communist rhetoric appealed to many Americans who feared Soviet influence. Reagan’s bold language—calling the USSR the “Evil Empire”—and his defense buildup projected strength and resolve.
Public Perception of Strength
For those asking why is Reagan Bush ’84 so popular, the answer must include the perception that Reagan was rekindling American power abroad. Many voters believed that strong leadership in foreign affairs would not only improve national security but also restore national pride.
The Bush Factor: Continuity and Trust
Although Reagan was the dominant figure in the ticket, Vice President George H.W. Bush played an important role in the campaign. Bush helped balance the ticket with his experience in government and foreign policy. His presence signaled continuity and stability within the administration.
Bush’s Appeal Across the Political Spectrum
Bush’s credentials, including roles as CIA Director and envoy to China, boosted voter confidence. For undecided or moderate voters, the Reagan Bush ’84 ticket represented a blend of bold leadership and seasoned experience—fueling its broader popularity.
Media and Messaging in 1984
Reagan Bush ’84 is also remembered for its sophisticated use of media. Television advertising had become a standard tool in political campaigns by the 1980s, but Reagan’s team understood how to do it effectively. Campaign ads were polished, emotionally charged, and nationally persuasive—helping the public understand not just policies, but the personalities behind them.
Television’s Role in Shaping Popularity
Television brought Reagan’s speeches into living rooms across America. His relaxed demeanor, confident tone, and clear messaging were amplified by this medium. This intuitive use of modern media is part of the reason why Reagan Bush ’84 so popular, even decades later.
Competing Against the Opposition
In 1984, the Reagan Bush ticket faced Democratic challenger Walter Mondale and his running mate Geraldine Ferraro—the first woman nominated for national office by a major party. While Ferraro’s historic nomination made headlines, the overall Democratic message failed to capture public enthusiasm on the scale of the Reagan Bush campaign.
Policy vs. Personality
Mondale focused primarily on policy critiques—challenging Reagan’s economic plans and deficits—whereas Reagan’s campaign focused on optimism and national renewal. This contrast in approach played into the widespread appeal of Reagan Bush ’84.
A Landslide Victory: Numbers Speak Loudly
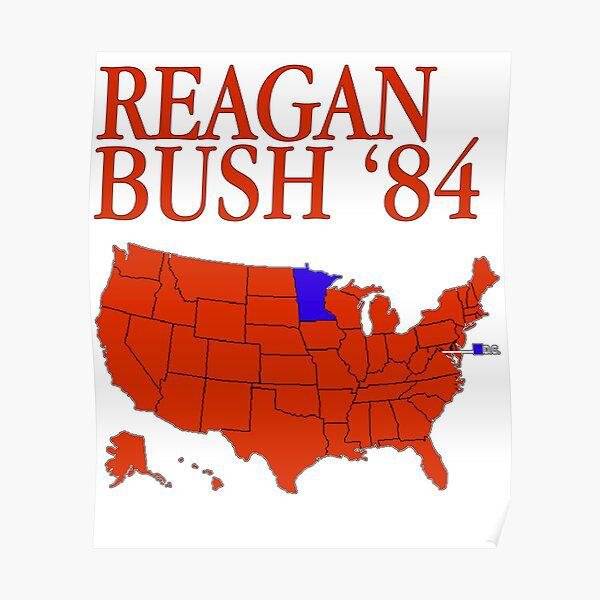
Fundamentally, why Reagan Bush ’84 is so popular can be seen in its electoral results. Reagan won 49 out of 50 states and nearly 59% of the popular vote. Such dominance in modern presidential elections is rare and suggests not just victory, but overwhelming public endorsement.
Public Mandate and Historical Memory
The margin of victory for Reagan Bush ’84 created a sense of mandate—a belief that the American people strongly supported Reagan’s vision. This perception solidified the campaign’s legacy in the years that followed.
Popular Culture and Reagan’s Legacy
Beyond political science textbooks, Reagan Bush ’84 has seeped into American cultural memory. Reagan’s speeches continue to be quoted, and his image remains influential among conservatives and many moderates alike. Cultural artifacts like campaign posters, slogans, and media references help explain ongoing interest.
Reagan’s Enduring Presence
Reagan’s popularity didn’t stop after his presidency. He became a symbol of conservative leadership, and his approach to public communication has influenced generations of politicians. This cultural footprint answers part of the question why is Reagan Bush ’84 so popular: it transcended its era and became part of the American narrative.
Critiques and Controversies
While Reagan Bush ’84 remains popular in many circles, it’s important to address criticisms. Some scholars point to rising deficits and economic inequality during the era. Others question aspects of Reagan’s foreign policy. These debates show that popularity does not equal universal agreement—but they also highlight how contested political legacies can sharpen historical interest.
The Long View: Why It Matters Today
In assessing why Reagan Bush ’84 remains popular, we should ask: what does this election teach us about leadership, public sentiment, and political communication? In a polarized modern context, the campaign is often studied for lessons on messaging, economic strategy, and national identity.
A Template for Future Campaigns?
Modern candidates reference Reagan’s optimistic tone, and political strategists analyze the 1984 campaign’s effectiveness. Whether one agrees with Reagan’s politics or not, the question why is Reagan Bush ’84 so popular continues to spark meaningful discussion in political science and public life.
Conclusion
Reagan Bush ’84 is more than a historical footnote—it’s a defining moment in American political history. The campaign’s popularity stemmed from a rich combination of factors: Reagan’s leadership and communication skills, economic recovery, national security confidence, effective media use, and broad public appeal. By examining these dynamics, we gain insight not only into a single election but also into the forces that shape political popularity over time. Understanding why is Reagan Bush ’84 so popular helps illuminate how leadership, optimism, and national identity intersect in powerful ways.
5 Relevant FAQs (Questions + Answers)
1. Why did Reagan Bush ’84 win by such a large margin?
Reagan Bush ’84 won decisively due to a combination of strong economic growth, effective campaigning, Reagan’s charismatic leadership, and public confidence in his vision for America.
2. Was the economy the main reason Reagan Bush ’84 was so popular?
Yes, the improving economy was a major factor. After early recession, economic indicators improved, which made the public more receptive to Reagan’s optimistic message.
3. How did media influence popularity in the Reagan Bush ’84 campaign?
Television ads, speeches, and strategic messaging amplified Reagan’s communication strengths. Messaging focused on optimism rather than fear, making it appealing to many voters.
4. Did Reagan Bush ’84’s popularity last beyond the election?
Yes, the campaign’s legacy influenced political discourse for decades. Reagan’s style and messaging continue to be studied and referenced in modern politics.
5. Are there criticisms of Reagan Bush ’84’s popularity today?
Some critics point to economic disparities and budget deficits from the era. However, debates about policy have not diminished general historical interest in the campaign.